
Many display cable types connect a monitor to different devices. HDMI handles both video and audio, making it popular for TVs and computers. DisplayPort supports high resolutions and refresh rates, which gamers often need. DVI sends digital video signals to a monitor. VGA, an older cable, carries analog signals. USB-C and Thunderbolt offer fast data transfer and power delivery, supporting modern monitors. Each cable type fits specific needs, so knowing the differences between these display cable types helps users choose the right cable for their monitor setup.
Key Takeaways
-
HDMI and DisplayPort cables support high resolutions and refresh rates, making them ideal for gaming and professional monitors.
-
USB-C and Thunderbolt cables offer video, data, and power in one cable, perfect for modern laptops and multi-monitor setups.
-
Older cables like DVI and VGA lack audio support and have lower resolution limits, so they suit legacy devices only.
-
Always check your device ports and match the cable to your monitor’s resolution and refresh rate for the best performance.
-
Choosing certified, high-quality cables ensures reliable connections and future-proofs your setup as technology advances.
Display Cable Types Overview
HDMI
HDMI, or High-Definition Multimedia Interface, stands as one of the most common monitor cable types today. It transmits both video and audio signals through a single cable, making it ideal for TVs, gaming consoles, and computers. HDMI cables support a wide range of resolutions, from standard HD up to 8K with the latest versions. Fiber optic HDMI cables maintain signal quality over long distances, which is important for home theaters and professional displays. HDMI adapters allow connections to USB-C or DisplayPort ports, but these adapters often use DisplayPort signals internally. Most modern monitors include at least one HDMI port, ensuring broad compatibility.
| Cable Type | Supported Resolution | Refresh Rate | Bandwidth | HDMI Version | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard HDMI | Up to 1080i or 720p | 30Hz | 5 Gbps | 1.0 to 1.2a | HDTV, Blu-ray, media streamers |
| High Speed HDMI | Up to 1080p and 4K | 30Hz | 10 Gbps | 1.3 to 1.4a | Deep color, 3D graphics |
| Premium High Speed HDMI | Up to 4K with HDR | 60Hz | 18 Gbps | 2.0a, 2.0b | Ultra HD, gaming, design apps |
| Ultra High Speed HDMI | Up to 8K or 10K with HDR | 120Hz to 240Hz | 48 Gbps | 2.1 | Gaming, HDR TV |
Tip: Certified HDMI cables ensure reliable performance, especially for high resolutions and refresh rates.
DisplayPort
DisplayPort is a digital interface designed for high-performance monitors. It supports higher resolutions and refresh rates than HDMI in many cases, making it popular among gamers and professionals. DisplayPort cables can handle up to 8K resolution and 144Hz refresh rates with the latest standards. Many monitors use DisplayPort for daisy-chaining, which allows multiple screens to connect through a single cable. DisplayPort also works with adapters for HDMI, DVI, or VGA, increasing its flexibility. Cable quality and length affect signal integrity, so active cables are recommended for longer runs.
DVI
DVI cables transmit digital video signals and were once the standard for computer monitors. DVI does not carry audio, so users need a separate cable for sound. Most DVI cables support resolutions up to 1920x1200, but dual-link DVI can reach 2560x1600. Signal quality depends on cable length and construction. For longer distances, signal boosters or extenders may be necessary. Many monitors and graphics cards still include DVI ports for compatibility with older devices. Adapters allow DVI connections to HDMI or DisplayPort, but users should check for feature support.
VGA
VGA is an analog cable type that has served as a standard for monitors for decades. It supports lower resolutions, typically up to 640x480 pixels, and does not transmit audio. VGA cables are prone to signal degradation over longer distances, resulting in reduced image quality. Modern monitors rarely include VGA ports, but some legacy equipment still relies on this connection. Adapters can connect VGA to USB-C or HDMI, but image quality remains limited.
| Cable Type | Max Resolution | Audio Support | Signal Type | Max Length | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGA | 640x480 | No | Analog | ~5 meters | No audio, low resolution, signal loss |
USB-C and Thunderbolt
USB-C and Thunderbolt represent the most versatile monitor cable types available. USB-C cables can transmit video, data, and power through a single connector. Many modern monitors use USB-C for easy docking and charging. Thunderbolt builds on USB-C by offering higher data transfer rates, up to 40 Gbps for Thunderbolt 4, and supports daisy-chaining multiple monitors. Thunderbolt cables guarantee consistent performance and safety through mandatory certification. USB-C cables vary in capability, so users should check for features like DisplayPort Alternate Mode. Thunderbolt is preferred in professional environments where reliability and speed are critical.
| Feature | USB-C (USB 4) | Thunderbolt 4 |
|---|---|---|
| Connector Type | USB-C | USB-C |
| Max Data Transfer | Up to 40 Gbps (sometimes 20 Gbps) | 40 Gbps (guaranteed) |
| Power Delivery | Up to 100W | Up to 100W |
| Display Support | Up to two 4K or one 8K display | Two 4K or one 8K display (guaranteed) |
| Daisy-Chaining | Not native, needs hubs | Up to six devices |
| Typical Usage | Everyday devices, docking | Professional, high-performance setups |
Note: Thunderbolt cables offer the highest reliability for demanding monitor setups, while USB-C provides broad compatibility for most modern devices.
Monitor Cable Types Comparison

Resolution and Bandwidth
Monitor cable types differ greatly in their ability to handle high resolutions and fast refresh rates. Digital cables such as HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C, and Thunderbolt support much higher data rates than analog cables like VGA. This difference directly impacts display performance, especially for users who need sharp images or smooth motion.
The following table summarizes the resolution and bandwidth capabilities of the most common monitor cable types:
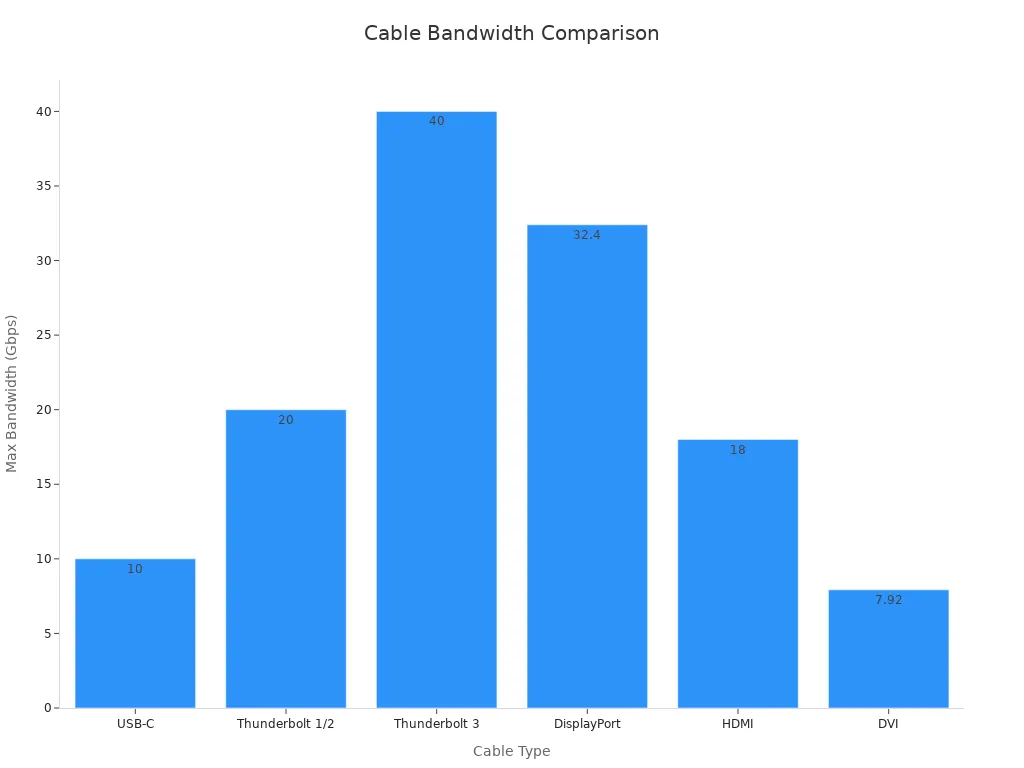
| Cable Type | Max Resolution | Max Refresh Rate | Max Bandwidth | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDMI 2.1 | 8K (7680×4320) | 120 Hz | 48 Gbps | Supports HDR, eARC, VRR, ALLM |
| HDMI 2.2 | 12K (12288×6480) | 120 Hz | 96 Gbps | Supports 16K at 60 Hz, full chroma, 10/12-bit |
| DisplayPort 1.4 | 8K (7680×4320) | 60 Hz | 32.4 Gbps | DSC, HDR, 30 bit/px color, daisy-chaining |
| DisplayPort 1.3 | 5K (5120×2880) | 60 Hz | 32.4 Gbps | Single cable 5K, 8K at 30 Hz |
| DVI (Dual-Link) | 2560×1600 | 60 Hz | 7.92 Gbps | Digital only, no audio |
| VGA | 1920×1200 (theoretical) | 60 Hz | N/A (Analog) | Analog, signal loss over distance |
| USB-C (DP Alt Mode) | 8K (with DP 1.4) | 60 Hz | Up to 40 Gbps | Video, data, power in one cable |
| Thunderbolt 4 | 8K (single display) | 60 Hz | 40 Gbps | Daisy-chaining, guaranteed performance |
Note: HDMI 2.1 and DisplayPort 1.4 both support 8K resolution, but HDMI 2.2 and Ultra96 HDMI cables push the limits even further, reaching up to 16K at 60 Hz.
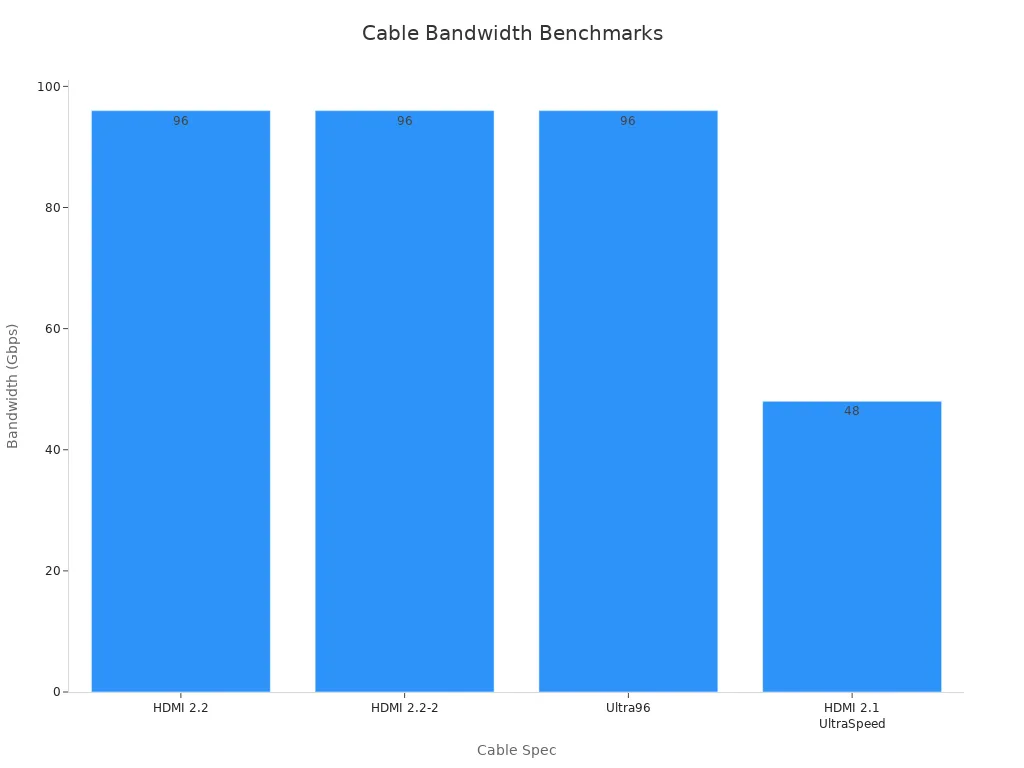
DisplayPort standards have evolved rapidly. For example, DisplayPort 1.4 supports 8K at 60 Hz with compression, while earlier versions required two cables for 5K at 60 Hz. HDMI 2.1 enables 8K at 120 Hz, making it a top choice for high-end gaming and professional monitors. In contrast, VGA and DVI cannot match these modern standards. VGA, being analog, suffers from signal degradation and lower clarity, especially at higher resolutions.
Audio Support
Audio support varies across monitor cable types. HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C, and Thunderbolt all transmit both video and audio signals, which simplifies setup for most users. DVI and VGA do not carry audio, so users must connect a separate audio cable when using these older standards.
Technical studies show that cable construction has little effect on audio quality for digital cables. Experts in audio engineering and psychoacoustics agree that most claims about premium cables improving sound are not supported by scientific evidence. Double-blind tests reveal that listeners cannot reliably distinguish between expensive and inexpensive cables. The main differences between cables relate to build quality and reliability, not to measurable improvements in sound.
Tip: For most users, any certified HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C, or Thunderbolt cable will deliver the same audio quality. Focus on cable certification and reliability rather than marketing claims about sound.
Compatibility
Compatibility plays a crucial role when choosing among monitor cable types. Modern monitors often include HDMI and DisplayPort ports, while USB-C and Thunderbolt are common on newer laptops and high-end displays. HDMI 2.1 and DisplayPort 1.4 offer broad compatibility with the latest gaming consoles, graphics cards, and monitors.
Older standards like VGA and DVI still appear on legacy equipment. VGA, being analog, does not work with many new monitors without adapters. DVI remains useful for connecting older computers to digital displays, but it lacks audio support and high refresh rates.
Thunderbolt and USB-C provide the most versatility. Thunderbolt 4 guarantees compatibility with demanding professional setups, supporting daisy-chaining and high data rates. USB-C, when equipped with DisplayPort Alternate Mode, allows users to connect a single cable for video, data, and power. However, not all USB-C cables support video output, so users should check device specifications.
| Cable Type | Digital/Analog | Audio Support | Modern Use | Legacy Use | Adapter Needed for New Devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDMI | Digital | Yes | Yes | Some | Rarely |
| DisplayPort | Digital | Yes | Yes | Rarely | Sometimes |
| DVI | Digital | No | Rarely | Yes | Often |
| VGA | Analog | No | No | Yes | Always |
| USB-C | Digital | Yes | Yes | No | Sometimes |
| Thunderbolt | Digital | Yes | Yes | No | No |
Note: Digital cables like HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C, and Thunderbolt offer the best compatibility with modern monitors. Analog cables such as VGA are now mostly limited to legacy systems.
Choosing the right monitor cable type ensures the best display performance and future-proofs your setup. Users should always consider the ports available on their devices, the required resolution and refresh rate, and whether audio support is necessary.
Choosing the Best Monitor Cable Type
Device Compatibility
Selecting the best monitor cable type starts with checking device compatibility. Every monitor and device has specific ports. Users should look at the available connections on both the monitor and the source device, such as a computer or gaming console. HDMI ports appear on most modern monitors, TVs, and laptops. DisplayPort is common on desktop monitors and graphics cards. Thunderbolt and USB-C ports are found on many new laptops and high-end monitors.
-
ManageEngine OpManager helps users monitor device connectivity and cable performance. It tracks metrics like bandwidth, uptime, and interface health. Real-time graphs and alarms alert users to cable or port issues, making it easier to spot compatibility problems.
-
The Total Phase Advanced Cable Tester v2 checks cable health and performance. It tests HDMI, DisplayPort, and USB cables for signal integrity and compatibility with power delivery standards. This tool helps users confirm that a cable will work with their devices.
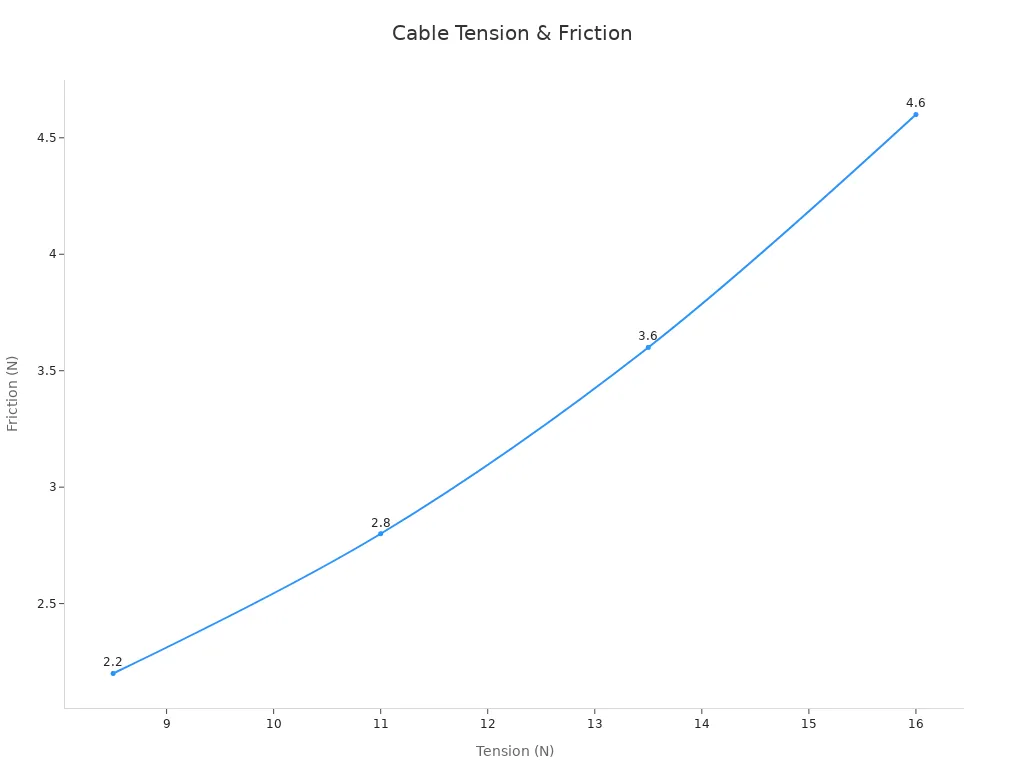
A table below shows how cable tension affects performance in specialized environments, such as fMRI-compatible setups. The data highlights the importance of choosing the right cable for the device and use case.
| Cable Tension (N) | Static Friction Force (N) |
|---|---|
| 8.5 | 2.2 |
| 11 | 2.8 |
| 13.5 | 3.6 |
| 16 | 4.6 |
Selecting a cable with the right tension and build quality prevents slack and ensures reliable operation. This approach applies to all environments, from offices to gaming setups.
Resolution and Refresh Rate Needs
The best monitor cable type depends on the resolution and refresh rate required. Gamers and creative professionals often need high resolutions and fast refresh rates. HDMI 2.1 supports up to 8K resolution at 120 Hz, making it ideal for gaming and home theater systems. DisplayPort also handles high resolutions and refresh rates, especially in multi-monitor setups.
-
HDMI 2.1 cables deliver high bandwidth, supporting advanced features like HDR and variable refresh rates. These features improve image quality and reduce screen tearing during fast-paced games.
-
DisplayPort cables work well for daisy-chaining multiple monitors. They support high refresh rates, which benefit users who need smooth motion and sharp visuals.
-
USB-C cables with DisplayPort Alt Mode allow users to connect laptops to monitors with a single cable. This setup provides video, data, and power, reducing clutter on the desk.
Tip: Always match the cable to the monitor’s maximum supported resolution and refresh rate. Using a lower-rated cable can limit performance, even if the monitor supports higher specs.
Future-Proofing
Future-proofing ensures that the best monitor cable type will remain useful as technology advances. Industry forecasts show steady growth in the audio and video cable market. The market size is expected to rise from USD 3.17 billion in 2024 to USD 4.63 billion by 2033, with a 4.3% CAGR. HDMI 2.1 leads the way, supporting up to 10K resolution and 48Gbps bandwidth. These features guarantee compatibility with future multimedia devices and gaming consoles.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2024) | USD 3.17 billion |
| Projected Market Size (2033) | USD 4.63 billion |
| CAGR (2025-2033) | 4.3% |
| Key Growth Drivers | HDMI 2.1 adoption, 4K/UHD TV demand, AI/IoT/AR/VR integration |
| Regional Highlights | Asia-Pacific: 5.9% CAGR; North America: 3.2% CAGR |
| Future-proofing Features | HDMI 2.1: higher bandwidth, refresh rates, emerging tech compatibility |
| Industry Trends | Multimedia device growth, digital signage, home entertainment |
Technological trends such as AI, IoT, and automation drive innovation in cable design. Manufacturers now focus on sustainability and green materials. Digital transformation and smart solutions keep cable products relevant. Business models like direct-to-consumer sales and subscriptions support changing market needs.
-
HDMI 2.1 cables offer the best future-proofing for most users. They support the latest standards and work with new devices.
-
Thunderbolt cables provide high reliability and performance for professional setups.
-
Choosing cables with certification and robust build quality ensures long-term use.
Note: Investing in a high-quality cable today can save money and hassle in the future. Users should consider not only current needs but also upcoming upgrades and new devices.
Display cable types differ in resolution, audio support, and compatibility. HDMI and DisplayPort work best for gaming and high-resolution displays. USB-C and Thunderbolt suit modern laptops and professional setups. DVI and VGA fit older devices. Users should check device ports and future needs before choosing a cable.
The right cable improves both display quality and user experience.
FAQ
What cable type works best for gaming monitors?
Gamers often choose DisplayPort or HDMI 2.1 cables. DisplayPort supports high refresh rates and resolutions. HDMI 2.1 also handles 4K at 120Hz. Both options deliver smooth gameplay and sharp images.
Can you use adapters to connect different cable types?
Yes, adapters connect HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI, or VGA ports. However, some adapters may limit resolution or features. Users should check device compatibility before buying an adapter.
Do all USB-C cables support video output?
Not all USB-C cables carry video signals. Only cables with DisplayPort Alternate Mode support video output. Users should look for this feature in device and cable specifications.
How long can a display cable be without losing quality?
Cable length affects signal quality. HDMI and DisplayPort cables work best under 15 feet (5 meters). Longer cables may need signal boosters or active cables to prevent image loss.
Written by Jack Elliott from AIChipLink.
AIChipLink, one of the fastest-growing global independent electronic components distributors in the world, offers millions of products from thousands of manufacturers, and many of our in-stock parts is available to ship same day.
We mainly source and distribute integrated circuit (IC) products of brands such as Broadcom, Microchip, Texas Instruments, Infineon, NXP, Analog Devices, Qualcomm, Intel, etc., which are widely used in communication & network, telecom, industrial control, new energy and automotive electronics.
Empowered by AI, Linked to the Future. Get started on AIChipLink.com and submit your RFQ online today!




