
Key Differences Between DDR4 and DDR5 RAM
Explore DDR4 vs DDR5 RAM differences in speed, capacity, and value.
| Features | DDR4 | DDR5 |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 3200-4000 MT/s | Starts at 4800 MT/s, up to 8400 MT/s |
| Maximum Capacity | Up to 32-64GB per DIMM | Up to 128-256GB per DIMM |
| Power Efficiency | Standard 1.2V voltage | Lower 1.1V with power management |
| Latency | Lower CAS latency (e.g., CL14) | Higher latency (e.g., CL38), offset by speed |
| Price | Generally lower cost | Higher cost, but prices dropping |
| Compatibility | Broad support on older systems | Requires latest CPUs and motherboards |
| Gaming Performance | Similar FPS, low latency advantage | Slight FPS boost in select games |
| Productivity Performance | Adequate for most tasks | Better for heavy multitasking and editing |
| Future-Proofing | Becoming outdated | Designed for next-gen systems |
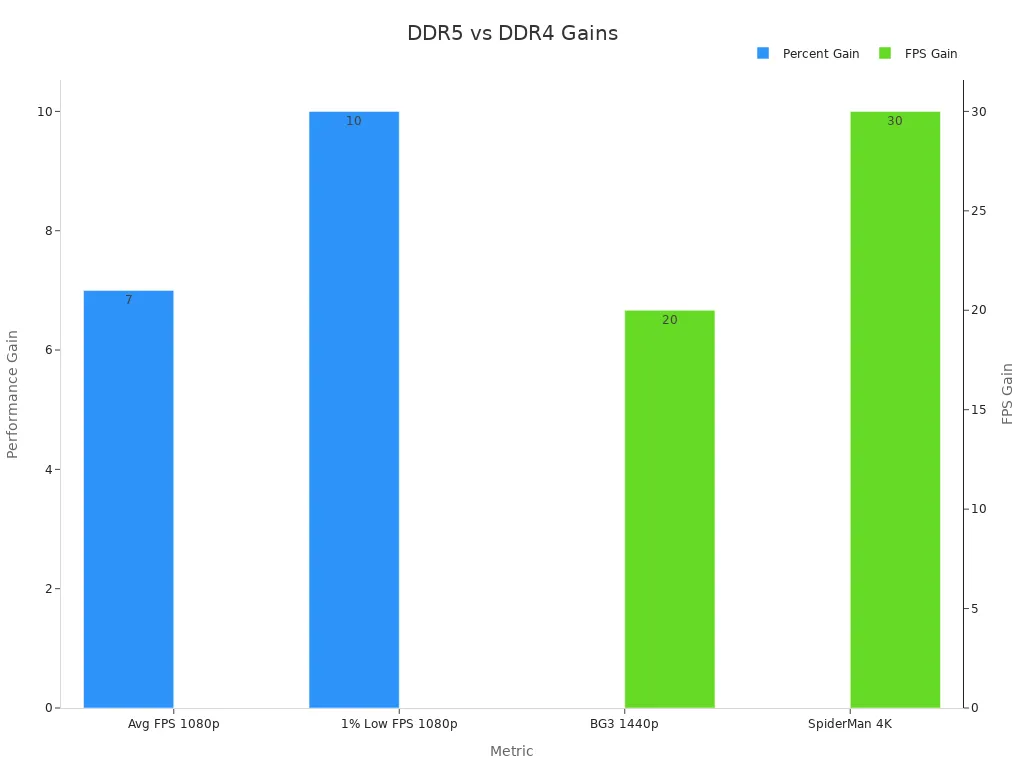
When comparing ddr4 vs ddr5, ddr5 offers higher speeds, better power efficiency, and greater memory capacity. For most users, upgrading to ddr5 random access memory brings about a 7% boost in average FPS at 1080p and up to 30 FPS more in some 1440p and 4K games, as shown below.
| Feature | DDR4 | DDR5 |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 3200-4000 MT/s | 4800 MT/s and above |
| Capacity per DIMM | Up to 32GB | Up to 128GB+ |
| Power Efficiency | Standard | Improved |
| Latency | Lower | Slightly higher |
| Price (32GB kit) | ~$170 | ~$130 |
Some users find ddr4 more compatible with current systems, while others see ddr5 as the best ram for future upgrades. Choosing between ddr4 vs ddr5 depends on each user's performance needs, system compatibility, and budget. Both types of ddr ram remain essential for gaming, productivity, and everyday memory tasks.
Key Takeaways
-
DDR5 RAM offers faster speeds, higher capacity, and better power efficiency than DDR4, making it ideal for heavy multitasking and future-proofing.
-
DDR4 RAM provides lower latency, broad compatibility, and better value for budget users, especially for gaming and everyday tasks.
-
Upgrading to DDR5 requires a compatible motherboard and CPU, while DDR4 upgrades are simpler and often cheaper.
-
Gaming performance differences between DDR4 and DDR5 are small, but DDR5 can improve productivity in memory-heavy applications.
-
Users should choose RAM based on their system compatibility, budget, and performance needs to get the best value.
Pros and Cons
DDR4
DDR4 remains a popular choice for many users. It offers strong compatibility with a wide range of motherboards and CPUs. Most systems built in the last several years support DDR4 RAM, making upgrades simple and cost-effective. DDR4 delivers reliable performance for gaming, productivity, and everyday computing. Many users find DDR4 RAM optimal for gaming at speeds around 3600MHz, where it provides low latency and stable frame rates up to 1440p resolution.
DDR4’s lower CAS latency, such as CL14 at 3600MHz, helps reduce delays in data access. This feature benefits both gamers and professionals who need fast response times.
A key advantage of DDR4 lies in its price-to-performance ratio. DDR4 RAM typically costs less than DDR5 RAM, making it attractive for budget-conscious buyers. Real-world benchmarks show that DDR4 achieves similar FPS in many games compared to DDR5, with CS:GO averaging 832 FPS on DDR4 versus 828 FPS on DDR5. Productivity tasks also see strong results, with DDR4 configurations reducing virtual machine latency by over 35% and doubling OLTP database processing rates when moving from 2133MHz to 3200MHz modules.
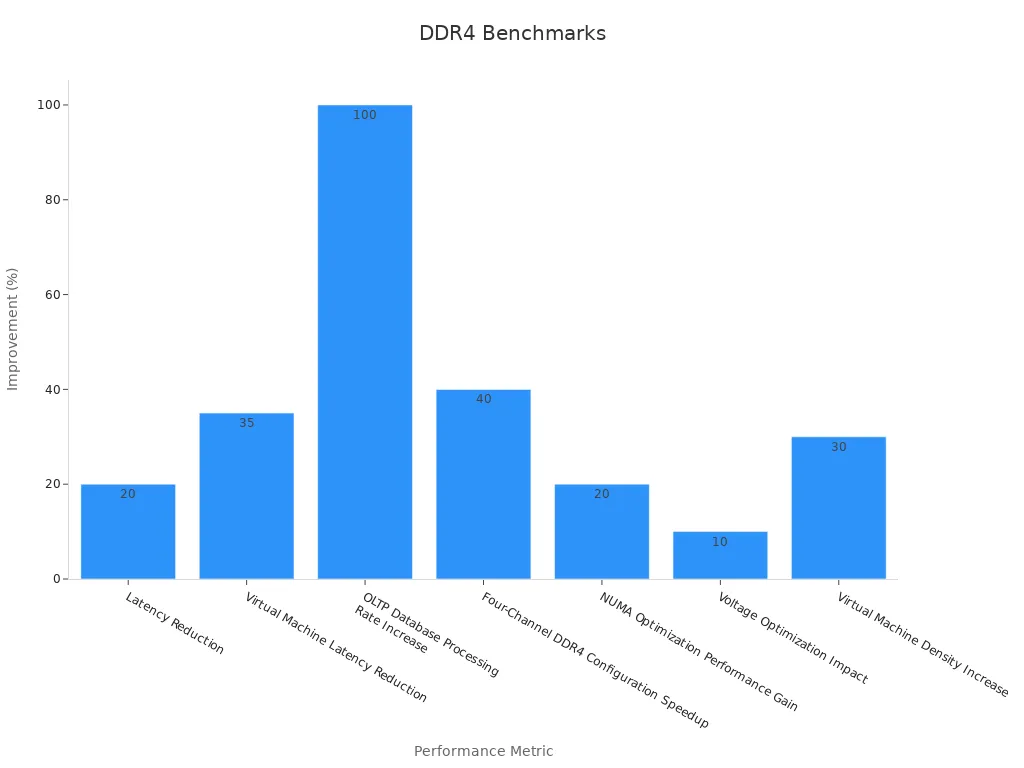
However, DDR4 is becoming less compatible with the latest CPUs and motherboards, which now favor DDR5. Its maximum capacity per stick usually tops out at 32GB, limiting future expansion for some users.
DDR5
DDR5 introduces several advancements over DDR4. It starts at higher speeds, with modules beginning at 4800 MT/s and reaching up to 8400 MT/s. DDR5 RAM supports greater capacity per stick, up to 64GB or more, which benefits users running memory-intensive applications or large multitasking workloads.
DDR5’s lower voltage (1.1V) and integrated power management improve efficiency, although real-world power savings remain a topic of debate.
DDR5 RAM offers higher bandwidth and transfer speeds, resulting in about a 6% performance boost in some workloads. This improvement becomes more noticeable in tasks that require heavy data processing or future software updates. DDR5 also provides better future-proofing, as new CPUs and motherboards increasingly support only DDR5.
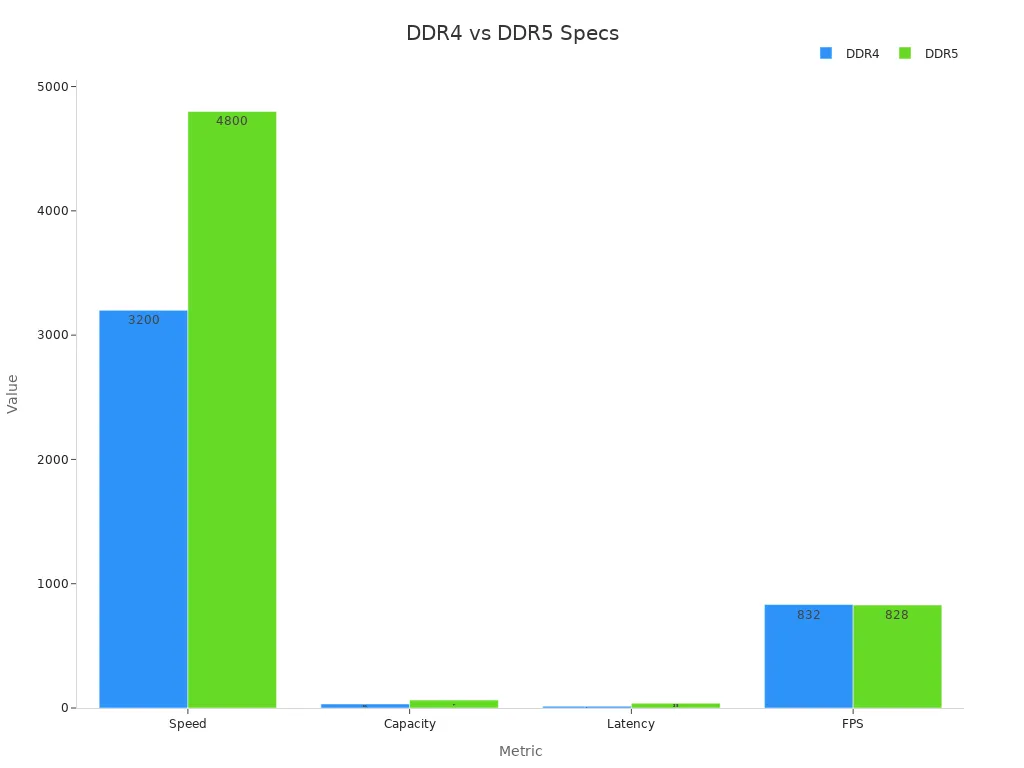
Despite these benefits, DDR5 comes with higher latency, such as CL38 at 5200MHz, which can offset some speed gains in certain scenarios. Gaming performance differences between DDR4 vs DDR5 remain small, with minimal FPS gains in most titles. DDR5 RAM also costs more, and the value for money may not justify an upgrade for every user at this stage.
| Aspect | DDR4 RAM | DDR5 RAM |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Speed | Up to 3200 MT/s | Starting at 4800 MT/s, potential up to 8400 MT/s |
| Maximum Capacity per Stick | 32 GB | 64 GB |
| Latency | Lower CAS latency (e.g., CL14 at 3600MHz) | Higher latency (e.g., CL38 at 5200MHz), offset by higher speeds |
| Performance Boost | Adequate for most gaming and productivity tasks; sometimes better value | ~6% performance boost in some workloads; higher bandwidth and transfer speeds |
| Gaming FPS Difference | Marginal differences; e.g., CS:GO average FPS ~832 (DDR4) vs ~828 (DDR5) | Similar FPS to DDR4 in many games; minimal gains in real-world gaming benchmarks |
| Productivity Benchmarks | Mixed results; sometimes DDR4 faster or similar | Slightly better in some tasks but sometimes slower; benefits depend on workload |
| Price | Lower cost, better price-to-performance ratio | Higher price, diminishing returns for cost currently |
| Compatibility | Becoming incompatible with newer CPUs | More future-proof, compatible with latest CPUs |
| Power Efficiency | Standard voltage (1.2V) | Lower voltage (1.1V) with integrated PMIC, but power savings debated |
DDR4 vs DDR5 Specifications
Speed and Bandwidth
Speed and bandwidth play a major role in how well a computer handles demanding tasks. DDR4 modules typically operate between 1600 and 3200 MT/s, while DDR5 starts at 4200 MT/s and can reach up to 8400 MT/s. This jump in speed allows DDR5 memory to deliver higher speeds and bandwidth, which means faster data transfer and improved multitasking. For example, DDR4-2400 offers a theoretical bandwidth of 19.2 GB/s with two DIMMs, but DDR5-5600 can reach 44.8 GB/s with the same number of modules. Manufacturers have already announced DDR5 RAM modules that run at 8000 MT/s or more, showing the potential for even greater performance.
DDR5's higher speeds and bandwidth make it ideal for users who need rapid data transfer, such as gamers and professionals working with large files.
-
Top read and write speeds for DDR5 often double those of DDR4.
-
DDR5 memory also uses a dual-channel architecture per DIMM, which improves memory access efficiency and boosts the data transfer rate.
Capacity
Capacity determines how much data a system can handle at once. DDR4 DIMMs support up to 32 GB per module, while DDR5 DIMMs can reach up to 128 GB per stick. This fourfold increase in capacity comes from higher-density memory chips and a new architecture. Users who run virtual machines, edit large videos, or use memory-intensive applications benefit most from this upgrade. DDR5 memory enables systems to support much larger memory pools, making it a better choice for future-proofing and heavy workloads.
| Memory Type | Maximum Capacity per Module |
|---|---|
| DDR4 | 32 GB |
| DDR5 | 128 GB |
Power Efficiency
Power efficiency affects both energy use and heat output. DDR4 operates at 1.2 volts, while DDR5 reduces this to 1.1 volts. This lower voltage leads to about 10-15% less energy consumption under similar workloads. DDR5 DIMMs also include integrated power management chips, which help regulate power more efficiently and reduce heat. These improvements matter most in environments with many memory modules, such as data centers, but they also benefit desktop users by lowering electricity costs and keeping systems cooler.
| Memory Type | Voltage (V) |
|---|---|
| DDR4 | 1.2 |
| DDR5 | 1.1 |
-
DDR5 RAM's integrated power management reduces power consumption and heat.
-
DDR4 memory remains a solid choice for users who prioritize budget over maximum efficiency.
Latency
Latency measures the delay before data moves from memory to the processor. DDR4 offers lower latency, especially at popular speeds like 3200 MT/s with CAS latency values as low as CL14. DDR5 starts with higher latency, such as CL38 at 5200 MT/s, but its dual-channel architecture per DIMM helps offset some of this delay. While DDR4 memory provides lower latency and widespread compatibility, DDR5's improvements in speed and bandwidth can compensate for the higher latency in many real-world scenarios.
Users who need the lowest possible latency, such as competitive gamers, may still prefer DDR4. However, DDR5's architectural changes continue to close the gap as speeds increase.
| Metric | DDR4 | DDR5 |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range (MT/s) | 1600 to 3200 | 4200 to 7200 (up to 8400) |
| Theoretical Bandwidth | DDR4-2400: 19.2 GB/s (2 DIMMs) | DDR5-5600: 44.8 GB/s (2 DIMMs) |
| Operating Voltage (V) | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| Channel Architecture | Single 72-bit channel | Dual 40-bit channels per DIMM |
| Latency Impact | Single channel access | Dual channels improve access efficiency |
Performance

Gaming
Gamers often look for the best possible gaming performance when choosing between DDR4 and DDR5. DDR5 offers higher speeds and bandwidth, which can lead to smoother gameplay in some scenarios. However, most current games do not fully utilize the extra bandwidth provided by DDR5. In many popular titles, DDR4 delivers frame rates that closely match those of DDR5, especially at 1080p and 1440p resolutions. For example, competitive shooters and eSports games show only a small difference in average FPS between the two memory types.
DDR5 can provide a modest performance gain of about 5-10% in select games, especially those optimized for newer hardware or higher resolutions. Some AAA games at 4K may see up to 30 FPS more with DDR5, but these cases remain rare. DDR4 still offers low latency, which benefits gamers who value fast response times. Most gaming PCs today run smoothly with DDR4, making it a reliable choice for budget-conscious players.
Note: Upgrading to DDR5 may become more important as future games demand more memory bandwidth and higher capacities.
Productivity
Productivity tasks often push memory to its limits, making the choice between DDR4 and DDR5 more significant. DDR5 stands out in this area due to its higher speeds, larger capacities, and improved architecture. Users working with video editing, 3D rendering, or scientific simulations will notice clear improvements in performance.
-
DDR5 shows nearly 11% faster performance in DaVinci Resolve Extended.
-
Adobe Photoshop and After Effects run 12-17% faster with DDR5.
-
Firefox code processing is 12% faster using DDR5.
-
Processing tasks like CAD modeling, medical imaging, and geographical surveys are 24-33% faster with DDR5.
-
DDR5 provides up to 2x system memory bandwidth compared to DDR4, significantly improving bandwidth per CPU core, especially for multi-core CPUs common in productivity workloads.
-
DDR5’s improved architecture and higher speeds (launch speed 4,800MT/s vs DDR4 max 3,200MT/s) help overcome DDR4’s bandwidth limitations, enabling better performance in memory-intensive productivity applications.
The table below highlights some key benchmarks and technical specs:
| Metric / Application | DDR4 Specification / Result | DDR5 Specification / Result | Performance Difference / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Speed (MT/s) | 3200 | 4800 (starting), up to 8400 | DDR5 starts 50% faster, can reach much higher speeds |
| Bandwidth (GB/s) | 25.6 | 38.4 (initial), up to 64 | DDR5 offers significantly higher bandwidth |
| Maximum DIMM Capacity | 64 GB | 512 GB | DDR5 supports much larger memory modules |
| Operating Voltage (V) | 1.2 | 1.1 | DDR5 is more power efficient |
| y-cruncher Benchmark | DDR4-4000 C16 | DDR5-6400 C36 | DDR5 is 25% faster |
| Adobe Lightroom | Baseline | DDR5 runs 28% faster | Significant improvement in photo editing tasks |
| Adobe Premiere | Baseline | DDR5 improves by 3% | Moderate gain in video editing |
| Adobe Photoshop | Baseline | Less than 1% difference | Minimal gain in lighter tasks |
These results show that DDR5 brings the most noticeable improvements in memory-intensive and professional applications. Users who rely on heavy multitasking or large datasets will benefit most from DDR5’s performance.
Everyday Use
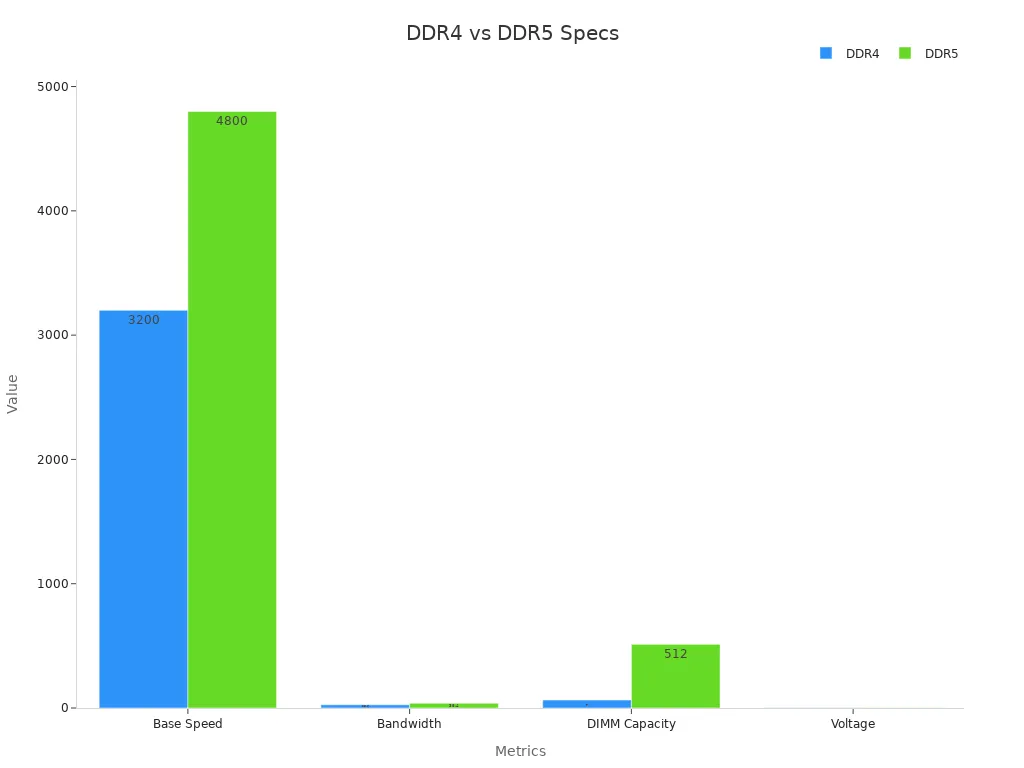
For everyday computing, such as web browsing, office work, and streaming, both DDR4 and DDR5 provide a smooth experience. DDR5 memory starts at 4800 MT/s, which is much faster than DDR4’s maximum of 3200 MT/s. High-end DDR5 modules can exceed 6000 MT/s, allowing for better multitasking and faster data handling in demanding applications. DDR5 also supports larger module capacities, up to 256GB per stick, compared to DDR4’s 64GB limit. This scalability helps users who plan to upgrade their systems for future needs.
DDR5 operates at 1.1V, making it more power efficient than DDR4’s 1.2V. This improvement reduces energy consumption and heat output, which is especially useful for laptops and compact desktops. Real-world benchmarks show DDR5-6400 C36 outperforming DDR4-4000 C16 by 25% in y-cruncher, while Adobe Lightroom runs 28% faster and Adobe Premiere improves by 3%. Adobe Photoshop shows minimal gains, indicating that lighter tasks do not benefit as much from DDR5.
Compatibility
Motherboards and CPUs
Compatibility between DDR4 and DDR5 depends on both the motherboard and the CPU. Most modern motherboards support only one type of memory, so users must check their system’s specifications before upgrading. DDR4 remains widely compatible with many motherboards and CPUs released in the past several years. Many users find it easy to upgrade or replace DDR4 modules because of this broad support.
In contrast, DDR5 support appears mainly in the latest chipsets from Intel and AMD. These new motherboards enable higher memory speeds, sometimes reaching up to 8800 MT/s. The table below shows how different motherboard models support various DDR5 speeds:
| Motherboard Model | DDR5 Speed Support (MT/s) |
|---|---|
| X870E Aorus Xtreme | Up to 8800 |
| X870E Aorus Master | Up to 8600 |
| X870E Godlike | 8400+ (1DPC 1R) |
| X870E Carbon | 8400+ (1DPC 1R) |
| X870E Taichi / Taichi Lite | 8200+ |
| X870E Nova | 8200+ |
| X870E Aorus Elite | 8200 |
| ProArt X870E Creator | 8000+ |
| Strix X870E-E | 8000+ |
Motherboard and CPU compatibility with DDR5 depends on matching the RAM speed to what the system supports. If a user installs DDR5 memory rated for higher speeds than the motherboard or CPU can handle, the system will run the RAM at a lower speed. This situation is similar to how DDR4 and even older DDR2 memory worked. BIOS updates and improvements from manufacturers continue to expand DDR5 compatibility, but users should always check for the latest support lists.
Tip: Users should always verify both motherboard and CPU support before purchasing new memory.
Upgrading
Upgrading from DDR4 to DDR5 requires more than just swapping out memory sticks. DDR4 and DDR5 use different physical connectors, so they are not interchangeable. Users who want to upgrade to DDR5 must purchase a compatible motherboard and a supported CPU. This requirement makes the upgrade process more involved and potentially more expensive.
DDR4 remains a strong choice for users who want a simple upgrade path. Many existing systems can accept higher-capacity or faster DDR4 modules without changing other components. DDR5, on the other hand, offers better future-proofing but requires a full platform upgrade. As more motherboards and CPUs support DDR5, the transition will become easier. Industry leaders like Intel and AMD have already started integrating DDR5 support into their latest products, and broader adoption is expected to accelerate through 2024.
Performance gains from DDR5 depend on the workload and the supported memory speed. Some tasks benefit from higher DDR5 speeds, but others see only small improvements compared to DDR4. Users should weigh the cost and complexity of upgrading against their actual needs.
Cost and Value
Pricing
When comparing pricing, ddr4 and ddr5 show clear differences. DDR4 memory prices have reached historically attractive levels. Many organizations see this as a strong buying opportunity for cost-effective, high-performance memory. Recent market data shows that ddr4 spot prices increased by about 12.8% in May 2025, reaching $2.46 per unit. This rise came as OEMs stockpiled ahead of tariffs. However, forecasts predict that ddr4 prices may decline by 5–10% later in 2025 as contract prices catch up.
DDR5, on the other hand, entered the market with premium pricing. Suppliers have shifted production capacity from ddr4 to ddr5, which has helped stabilize ddr5 prices. Still, ddr5 adoption remains slower than expected due to availability challenges and higher costs. Geopolitical tensions and supply chain issues have also influenced both ddr4 and ddr5 pricing. The market now sees a split: ddr4 faces oversupply and price drops, while ddr5 grows in demand for AI and data center applications.
A quick look at current consumer pricing:
| Aspect | DDR4 RAM | DDR5 RAM |
|---|---|---|
| Price (16GB kit) | Under $40 | Around $70 |
| Price (32GB kit) | Historically higher | About $90 (now cheaper than DDR4 at this capacity) |
| Motherboard cost difference | Slightly cheaper or parity | Slightly more expensive, but gap closing |
Value for Money
Value for money depends on user needs and system requirements. DDR4 offers better value for budget-conscious buyers. It provides fast performance for most everyday tasks and gaming. Many users find that ddr4 ram meets their needs without extra expense. DDR4 is also a strategic choice for those looking to upgrade existing systems, especially with current favorable pricing.
DDR5 brings higher speeds, greater bandwidth, and improved energy efficiency. These benefits become more noticeable in heavy workloads like video encoding or 3D rendering. For users who want future-proof systems or plan to run demanding applications, ddr5 offers a clear advantage. At higher capacities, ddr5 is now sometimes cheaper than ddr4, making it more attractive for new builds.
Tip: Users should consider their workload and upgrade plans. DDR4 remains the best value for most, while ddr5 is ideal for those seeking top performance and future readiness.
Future-Proofing with DDR5 RAM
Longevity
DDR5 stands out as a future-proof choice for users who want their systems to last. The technology uses advanced DRAM process nodes, such as D1z and D1a, which allow for higher density and better performance. Manufacturers like Samsung and SK Hynix have introduced new techniques, including high-k metal gate and EUV-based chips, to push DDR5 even further. These innovations help DDR5 achieve bandwidths up to 44.8 GB/s, which is over 30% faster than DDR4.
DDR5 dimm modules operate at a lower voltage of 1.1V, compared to DDR4’s 1.2V. This lower voltage reduces power consumption and heat, which can extend the lifespan of each dimm. DDR5 also supports much larger capacities, with dimm sizes reaching up to 128GB and even 256GB in the future. This scalability means that users can upgrade their systems with more memory as their needs grow.
Other features, such as on-die error correction and improved power management, make DDR5 more reliable for demanding workloads. These improvements help DDR5 handle heavier tasks and support the needs of next-generation computing. As a result, DDR5 dimm modules offer better longevity and reliability than previous memory standards.
Who Should Upgrade
Not every user needs to upgrade to DDR5 right away. However, certain groups will benefit more from early adoption:
-
Power users and professionals: Those who work with AI, machine learning, big data, or video editing will see the most gains. DDR5 dimm modules provide the bandwidth and capacity needed for these tasks.
-
Gamers and enthusiasts: Users who want the latest technology and plan to build high-end systems will find DDR5 a smart investment. DDR5 dimm modules support higher speeds and future CPU platforms.
-
Businesses and data centers: Organizations that rely on cloud computing or large databases need scalable solutions. DDR5 dimm modules offer the capacity and efficiency required for these environments.
Market forecasts show strong growth for DDR5. The DDR5 dimm socket market is expected to grow from USD 329 million in 2024 to over USD 1 billion by 2031. This growth is driven by the need for high-performance computing in many industries. DDR5 dimm modules also support energy efficiency and enhanced data security, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Tip: Users planning to keep their systems for several years or who expect to run memory-intensive applications should consider DDR5 dimm modules for better future-proofing.
Choosing between DDR4 and DDR5 depends on user needs. Gamers and budget users often find DDR4 the best ram for value and compatibility. Professionals who need higher performance in memory-heavy tasks benefit more from DDR5. The table below highlights the main differences:
| Aspect | DDR4 | DDR5 |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 3200 MT/s | Up to 6400 MT/s |
| Capacity | Up to 64 GB | Up to 256 GB |
| Cost per GB | Lower | Higher |
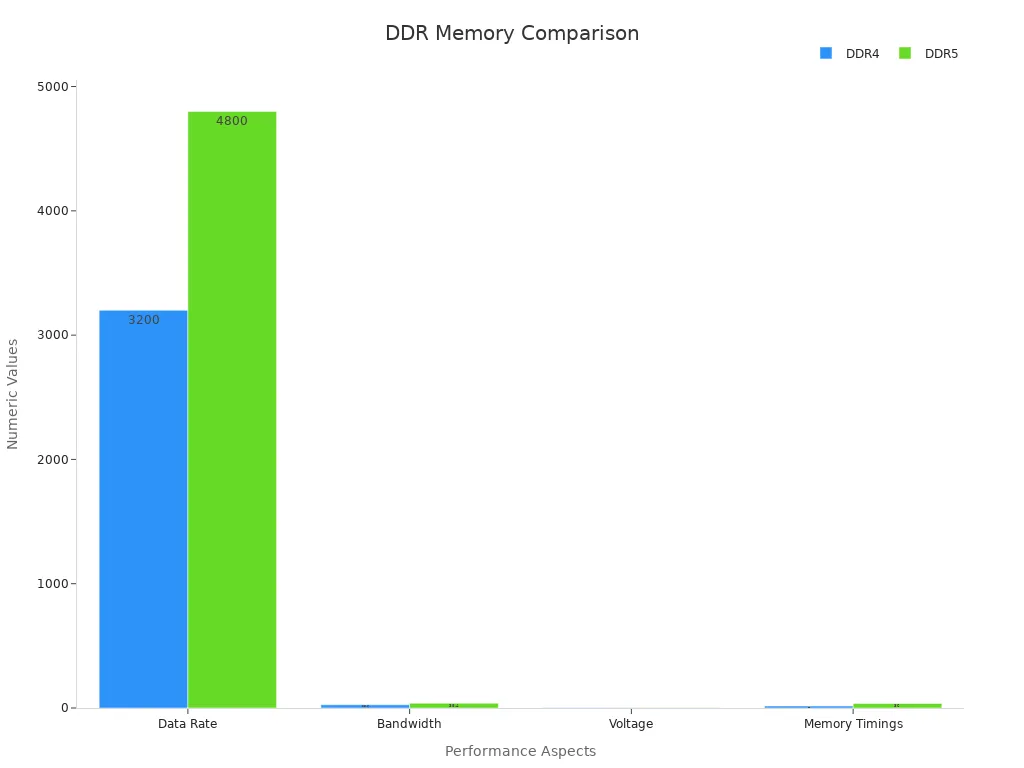
Users should match RAM choice to system compatibility, cost, and future-proofing. Each option offers strengths for different scenarios.
FAQ
What is the main difference between DDR4 and DDR5 RAM?
DDR5 RAM offers higher speeds, greater bandwidth, and larger capacities than DDR4. DDR4 provides lower latency and broader compatibility with older systems. Users should compare their needs before choosing.
Does DDR5 RAM improve gaming performance over DDR4?
DDR5 can boost gaming performance by 5–10% in some titles. Most games show only small differences. Gamers who want the best value may still choose DDR4.
Can users install DDR5 RAM in a DDR4 motherboard?
No. DDR4 and DDR5 use different connectors. Users must have a compatible motherboard and CPU for DDR5 RAM.
Is DDR5 RAM worth the extra cost for everyday tasks?
For basic tasks like web browsing or office work, DDR4 and DDR5 perform similarly. DDR5 becomes more valuable for heavy multitasking or future upgrades.
Written by Jack from AIChipLink.
AIChipLink, one of the fastest-growing global independent electronic components distributors in the world, offers millions of products from thousands of manufacturers, and many of our in-stock parts is available to ship same day.
We mainly source and distribute integrated circuit (IC) products of brands such as Broadcom, Microchip, Texas Instruments, Infineon, NXP, Analog Devices, Qualcomm, Intel, etc., which are widely used in communication & network, telecom, industrial control, new energy and automotive electronics.
Empowered by AI, Linked to the Future. Get started on AIChipLink.com and submit your RFQ online today!














